Choosing the right cloud platform is a critical decision for any business. The market leaders—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure— each offer a vast array of services, from basic computing and storage to advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence. This comprehensive comparison will delve into the core offerings of AWS, GCP, and Azure, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and pricing models. Understanding these key differences is essential for selecting the platform that best aligns with your specific business needs, technical requirements, and budget constraints. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of choosing between AWS vs Azure vs GCP.
This article provides a detailed comparison of AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure across several key areas, including compute, storage, networking, databases, security, and pricing. Whether you are a startup looking for a cost-effective solution or an enterprise seeking a robust and scalable platform, this comparison will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision. We’ll explore the benefits and drawbacks of each platform, helping you determine whether the expansive ecosystem of AWS, the innovative data analytics capabilities of GCP, or the enterprise-friendly integrations of Azure are the best fit for your organization. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the AWS vs Azure vs GCP landscape and be better prepared to select the ideal cloud provider for your unique requirements.
Overview of the Top Three Cloud Providers
The cloud computing market is dominated by three major players: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. Each provider offers a comprehensive suite of services, catering to a wide range of needs from basic computing and storage to advanced analytics and artificial intelligence.
AWS, the pioneer and current market leader, boasts the most mature platform with the widest range of services. It offers a robust global infrastructure and a massive partner ecosystem. AWS is known for its pay-as-you-go pricing model and extensive documentation.
Google Cloud Platform leverages Google’s expertise in data analytics and machine learning. GCP is known for its innovative services in these areas, as well as its competitive pricing and commitment to open source technologies.
Microsoft Azure benefits from its deep integration with Microsoft’s existing enterprise software ecosystem. Azure is a strong choice for organizations heavily invested in Microsoft technologies, offering seamless integration and a familiar management experience.
Core Features of AWS, GCP, and Azure
Each cloud provider offers a comprehensive suite of services. Compute services form the foundation, with AWS offering EC2, GCP providing Compute Engine, and Azure featuring Virtual Machines. These services allow users to deploy and manage virtual servers in the cloud.
Storage is another crucial component. AWS offers S3 for object storage, GCP provides Cloud Storage, and Azure features Blob Storage. These services enable users to store and retrieve data at scale.
Networking capabilities connect resources and enable communication. AWS offers Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), GCP provides Virtual Private Cloud (also VPC), and Azure features Virtual Network. These services allow users to create isolated networks within the cloud.
Databases are essential for many applications. AWS offers RDS and DynamoDB, GCP provides Cloud SQL and Cloud Spanner, while Azure offers SQL Database and Cosmos DB. These services cater to various database needs, from relational to NoSQL.
Finally, security features are paramount. All three providers offer robust security measures, including identity and access management (IAM), encryption services, and compliance certifications.
Pricing Models Compared
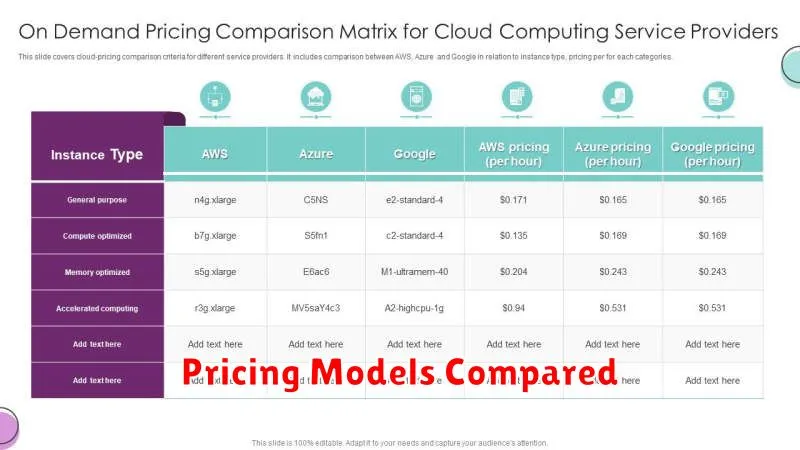
Understanding the pricing models of AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure is crucial for effective cloud cost management. While all three providers offer pay-as-you-go models, nuances exist that can significantly impact your overall expenses. Pay-as-you-go allows you to pay only for the resources consumed, offering flexibility and scalability.
Beyond pay-as-you-go, each provider offers various discount options. Reserved instances (AWS, Azure) and committed use discounts (Google Cloud) provide substantial cost savings for long-term commitments. Spot instances (AWS), preemptible VMs (Google Cloud), and spot VMs (Azure) offer deeply discounted rates for workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
Analyzing your workload requirements and leveraging the appropriate pricing model is essential for optimizing cloud costs. Free tiers are available across all three platforms, allowing experimentation and development at no cost, within specified usage limits. Carefully evaluating these options and utilizing cost management tools can help control and minimize your cloud expenditure.
Ease of Use and Developer Tools
A key consideration when choosing a cloud provider is the ease of use of its platform and the quality of its developer tools. Each of the major cloud providers—AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure—offers a different experience in this regard. AWS, while incredibly powerful and feature-rich, can be perceived as having a steeper learning curve, particularly for new users. Its extensive documentation and range of services can be overwhelming initially.
Google Cloud is often praised for its user-friendly console and focus on developer experience. Its well-designed command-line interface (CLI) and SDKs are generally considered intuitive and easy to use. Google Cloud’s strength in containerization and Kubernetes also makes it a popular choice for developers working with modern applications. Microsoft Azure, with its strong ties to the .NET ecosystem, offers a familiar environment for developers accustomed to Microsoft technologies. Its integration with Visual Studio and other Microsoft development tools can simplify the development and deployment process.
Ultimately, the best choice in terms of ease of use and developer tools depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user. Factors to consider include existing technical expertise, familiarity with particular programming languages or frameworks, and the specific tools and services required for the project.
Global Availability and Data Centers
A key consideration when choosing a cloud provider is the global reach of their services. Availability zones and regions are crucial components of this global infrastructure. Each provider divides its services across different geographic locations, allowing for redundancy and high availability.
AWS (Amazon Web Services) boasts a massive global presence, with a large number of regions and availability zones. This extensive network allows for low latency and disaster recovery options across the globe.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) also maintains a substantial global footprint, though generally fewer regions than AWS. GCP focuses on strategically placed data centers with robust interconnectivity.
Microsoft Azure, leveraging Microsoft’s existing infrastructure, has a strong and growing global presence. Its data center coverage focuses on key business hubs and provides excellent connectivity.
Choosing the right provider depends on the specific needs of your application or business. Consider factors such as the location of your users, regulatory requirements, and disaster recovery plans when evaluating the global availability offered by each provider.
Security and Compliance Standards

Security and compliance are paramount when choosing a cloud provider. AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure each maintain robust security postures and adhere to a wide range of compliance standards.
All three providers offer services for identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, network security, and security auditing. They also undergo regular third-party audits to validate their security controls.
While each provider covers major compliance certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPAA, specific certifications may vary. It’s crucial to verify that the chosen provider meets the specific compliance requirements of your industry and region.
Customers are responsible for configuring services securely and managing their own data in compliance with relevant regulations, regardless of the provider chosen.
Which Cloud Is Best for Your Project?
Selecting the right cloud provider—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure—depends heavily on your specific project needs. Each platform offers a robust suite of services, but their strengths lie in different areas.
AWS boasts the largest market share and offers the widest range of services, making it suitable for diverse projects. Its mature ecosystem and extensive documentation are beneficial for complex deployments. However, this breadth can also lead to complexity.
GCP excels in data analytics and machine learning, leveraging Google’s expertise in these fields. Its innovative services and competitive pricing make it attractive for data-intensive projects. However, its smaller market share might mean fewer readily available resources compared to AWS.
Azure integrates seamlessly with Microsoft products and services, making it a natural choice for organizations heavily reliant on the Microsoft ecosystem. Its strength in enterprise solutions and hybrid cloud deployments caters to specific business needs. However, its pricing structure can be more complex than AWS or GCP.
Ultimately, choosing the best cloud provider requires careful consideration of factors like project requirements, budget, existing infrastructure, and team expertise. A thorough evaluation of your specific needs against each provider’s strengths is crucial for project success.

