Have you ever wondered what exactly cloud computing is? Beyond the buzzword, it’s a transformative technology impacting our daily lives, from how we store photos to how businesses operate. This article provides a simple, beginner-friendly explanation of cloud computing, demystifying its core concepts and exploring its various forms, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). We’ll delve into the benefits of cloud computing, such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility, while also addressing potential security concerns.
Understanding cloud computing is increasingly essential in today’s digital world. Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or simply curious about technology, this guide will equip you with a foundational understanding of cloud computing principles. Learn how cloud computing works, its various applications, and its potential impact on your personal and professional life. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear grasp of what cloud computing is and why it matters.
Understanding the Basics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”). Instead of owning and maintaining your own physical infrastructure, you access these services on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
One of the key benefits of cloud computing is its scalability. You can easily increase or decrease your usage of these resources as your needs change, paying only for what you consume. This eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands.
There are three main deployment models for cloud computing: public cloud, where services are available to anyone over the internet; private cloud, where services are dedicated to a single organization; and hybrid cloud, which combines aspects of both public and private clouds.
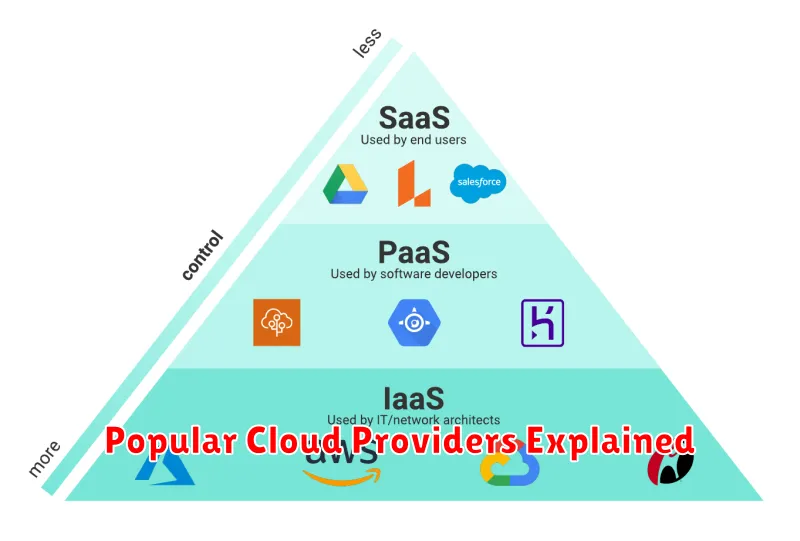
Furthermore, cloud computing services are typically offered in three main service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), providing access to basic computing resources; Platform as a Service (PaaS), offering a platform for developing and deploying applications; and Software as a Service (SaaS), delivering ready-to-use software applications over the internet. Understanding these fundamental concepts helps clarify the power and flexibility of cloud computing.
Types of Cloud Services: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Cloud computing services are broadly categorized into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each offers a different level of control and management responsibility.
With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure—servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis. You have the most control over the environment, but you are also responsible for managing the operating systems, applications, middleware, data, and runtime. This model offers great flexibility and control for businesses with specific IT requirements.
PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider takes care of the servers, storage, and networking, allowing developers to focus on coding and deployment. This option simplifies development and reduces operational overhead.
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. Users access these applications through a web browser or mobile app without having to install or manage any software locally. Examples include email clients, CRM software, and project management tools. SaaS offers the simplest and most convenient cloud computing model.
How Cloud Differs from Traditional Hosting
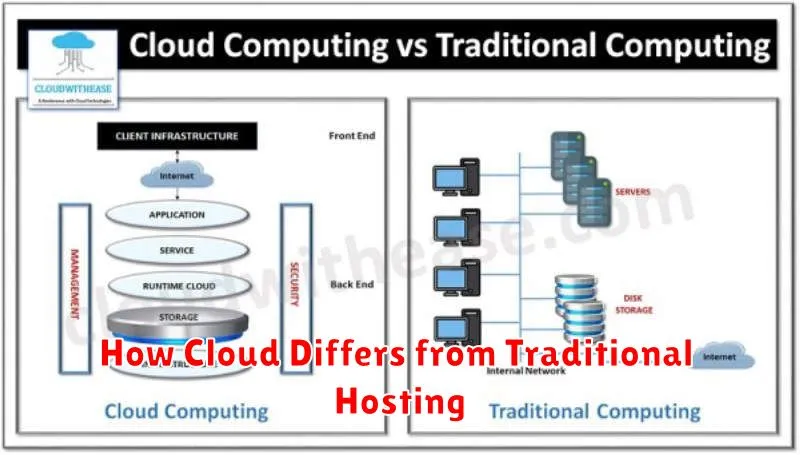
Traditional hosting relies on physical servers located in a data center. You purchase a specific amount of server resources, like RAM and storage. Whether you fully utilize these resources or not, you pay for the allocated capacity. This can lead to wasted resources and higher costs.
Cloud hosting, in contrast, leverages a network of virtualized servers. Resources are allocated dynamically based on demand. This scalability is a key differentiator, allowing you to easily increase or decrease resources as needed. You only pay for what you use, offering greater cost-efficiency.
Another critical difference lies in reliability. With traditional hosting, a hardware failure can lead to significant downtime. Cloud hosting mitigates this risk through redundancy. If one server fails, others seamlessly take over, ensuring minimal disruption.
Accessibility is also enhanced with cloud hosting. You can access your data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. Traditional hosting often ties you to specific locations or devices.
Key Benefits for Individuals and Businesses
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages for both individuals and businesses. For individuals, cloud storage provides a safe and accessible way to store files, photos, and videos, eliminating the need for physical hard drives and mitigating the risk of data loss due to hardware failure. Accessing data becomes effortless, achievable from any device with an internet connection.
Businesses benefit significantly from cloud computing’s scalability and cost-effectiveness. Instead of investing heavily in on-site infrastructure, companies can leverage cloud resources on demand, paying only for what they use. This flexibility allows businesses to easily adapt to changing needs and scale their operations quickly. Furthermore, cloud services often come with built-in security features, enhancing data protection and reducing the burden on internal IT teams.
Increased collaboration is another crucial benefit. Cloud-based platforms facilitate seamless teamwork, enabling multiple users to access and modify documents simultaneously, regardless of their location. This fosters productivity and streamlines workflows.
Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals interact with technology. Its versatility is showcased in a multitude of real-world applications across various sectors. For instance, in data storage and backup, cloud services offer scalable and secure solutions for individuals and enterprises alike, eliminating the need for physical hardware and mitigating the risk of data loss.
Software development and testing environments benefit significantly from cloud infrastructure. Developers can quickly deploy and scale resources, accelerating the development lifecycle. Cloud-based platforms also facilitate collaboration among geographically dispersed teams. Moreover, the entertainment industry leverages cloud computing for streaming services. Viewers can access content on demand, anytime and anywhere, across a range of devices. Cloud platforms manage the massive storage and bandwidth requirements, enabling seamless delivery of high-quality video and audio.
E-commerce platforms utilize cloud computing to manage online stores, process transactions, and handle customer data. The scalability of cloud resources allows businesses to adapt to fluctuating traffic demands, especially during peak shopping seasons. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems also often rely on cloud platforms. This allows for accessible customer data from anywhere, facilitating improved sales and customer service interactions. Cloud-based communication and collaboration tools, such as video conferencing and email, have become essential for remote work and team communication, enabling seamless connectivity and information sharing.
Popular Cloud Providers Explained
Several companies dominate the cloud computing market, offering a wide array of services. Understanding their strengths can help you choose the right provider for your needs. Three of the most popular cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
AWS is the current market leader, known for its comprehensive range of services and mature infrastructure. They offer everything from basic computing power to advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning tools.
Microsoft Azure is a strong contender, particularly appealing to businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. Azure seamlessly integrates with existing Microsoft products and offers robust enterprise-grade solutions.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is known for its innovation in data analytics and machine learning. GCP excels in providing cutting-edge technologies and is a popular choice for data-driven businesses and developers.
Future of Cloud Technology
The future of cloud computing promises continued growth and transformation across various sectors. Several key trends are shaping this evolution.
Serverless computing is gaining traction, abstracting away server management entirely and allowing developers to focus solely on code. This model enhances efficiency and scalability.
Edge computing is bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and enabling real-time applications like IoT devices and autonomous vehicles.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming deeply integrated with cloud platforms, offering powerful tools for data analytics, predictive modeling, and automation.
Increased focus on security and privacy is driving innovation in areas like confidential computing and blockchain integration, strengthening trust in cloud environments.
The rise of quantum computing, though still in its early stages, holds immense potential to revolutionize complex computations and simulations, opening new frontiers for scientific discovery and technological advancement.
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration, with cloud providers investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient infrastructure to minimize environmental impact.

